动态部署
动态部署是 ECSM 的一项重要功能。用户可以在部署阶段一次选择多个节点,ECSM 会根据节点负载情况动态部署容器镜像,以确保系统资源充分、均衡使用并保持微服务良好的运行状态。如果某个节点因为故障、断网或重启等原因导致服务异常,ECSM 会将容器镜像动态迁移到可用的节点上,从而保证业务的可用性和连续性。
前提条件
本节以安装 SylixOS 环境节点部署 C/C++ 容器镜像举例。
已有至少 2 个 SylixOS 的超边缘计算节点。
已安装 ECSM 。
代码示例
本次动态部署功能服务端模拟陀螺仪传感器场景,客户端订阅陀螺仪位置数据。通过查看客户端在服务端动态部署迁移前后接收的数据格式对比,展示验证动态部署功能。
服务端的代码示例 axis_server 模拟陀螺仪位置信息,当客户端订阅成功后,发送陀螺仪的位置信息。
客户端代码示例 axis_client 只订阅数据并在终端输出。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include "vsoa_server.h" #include "vsoa_platform.h" #define MY_SERVER_PASSWD "123456" static vsoa_server_t *server; /* * Publish axis thread */ static void *publish_axis_thread (void *arg) { vsoa_url_t url; vsoa_payload_t payload; char param[100]; int roll = 1, pitch = 1, yaw = 1; url.url = "/axis"; url.url_len = strlen(url.url); payload.data = NULL; payload.data_len = 0; payload.param = param; while (1) { sleep(1); if (!vsoa_server_is_subscribed(server, &url)) { continue; } payload.param_len = sprintf(param, "{\"roll\": %d, \"pitch\": %d, \"yaw\": %d}", roll++, pitch++, yaw++); vsoa_server_publish(server, &url, &payload); } return (NULL); } int main (int argc, char **argv) { int cnt, max_fd; fd_set fds; pthread_t id; struct sockaddr_in addr; struct timespec timeout = { 1, 0 }; bzero(&addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); addr.sin_family = AF_INET; addr.sin_port = htons(3002); addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; #ifdef VSOA_HAS_SIN_LEN addr.sin_len = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in); #endif /* * Initialize server */ server = vsoa_server_create("{\"name\":\"axis_server\"}"); if (!server) { fprintf(stderr, "Can not create VSOA server!\n"); return (-1); } /* * If need password */ vsoa_server_passwd(server, MY_SERVER_PASSWD); /* * Start server */ if (!vsoa_server_start(server, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in))) { vsoa_server_close(server); fprintf(stderr, "Can not start VSOA server!\n"); return (-1); } /* * Create publish thread */ pthread_create(&id, NULL, publish_axis_thread, NULL); while (1) { FD_ZERO(&fds); max_fd = vsoa_server_fds(server, &fds); cnt = pselect(max_fd + 1, &fds, NULL, NULL, &timeout, NULL); if (cnt > 0) { vsoa_server_input_fds(server, &fds); } } return (0); }#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <errno.h> #ifdef SYLIXOS #include <sys/vproc.h> #endif #include "vsoa_cliauto.h" /* My server password */ #define MY_SERVER_PASSWD "123456" /* My client */ static vsoa_client_t *client; /* My client auto */ static vsoa_client_auto_t *cliauto; /* My subscribe (string pointer array) */ static char *sub_urls[] = { "/axis" }; static void onconnect (void *arg, vsoa_client_auto_t *cliauto, bool connect, const char *info) { printf("On connect, connect: %s, info: %s\n", (connect == true) ? "connected" : "disconnected", info); } /* * On subscribed messages received */ static void onmessage (void *arg, struct vsoa_client *client, vsoa_url_t *url, vsoa_payload_t *payload, bool quick) { printf("On message, URL: %.*s payload: %.*s\n", (int)url->url_len, url->url, (int)payload->param_len, payload->param); } /* * main function */ int main (int argc, char **argv) { #ifdef SYLIXOS vprocExitModeSet(getpid(), LW_VPROC_EXIT_FORCE); #endif /* * Create client auto robot */ cliauto = vsoa_client_auto_create(onmessage, NULL); client = vsoa_client_auto_handle(cliauto); if (!vsoa_client_auto_setup(cliauto, onconnect, NULL)) { vsoa_client_auto_delete(cliauto); fprintf(stderr, "Cannot register connect callback: %s (%d)\n", strerror(errno), errno); return -1; } /* * Client auto robot start * The robot will automatically connect to the specified server and maintain the connection. * At this time, the developer only needs to focus on the business. */ vsoa_client_auto_start(cliauto, "vsoa://axis_server", MY_SERVER_PASSWD, (char * const)sub_urls, 1, 1000, 1000, 1000); while (true) { sleep(1); } }
操作步骤
动态部署容器镜像
在容器部署页面,单击服务列表左上方的新建,进入新建容器部署页面的基本信息界面。
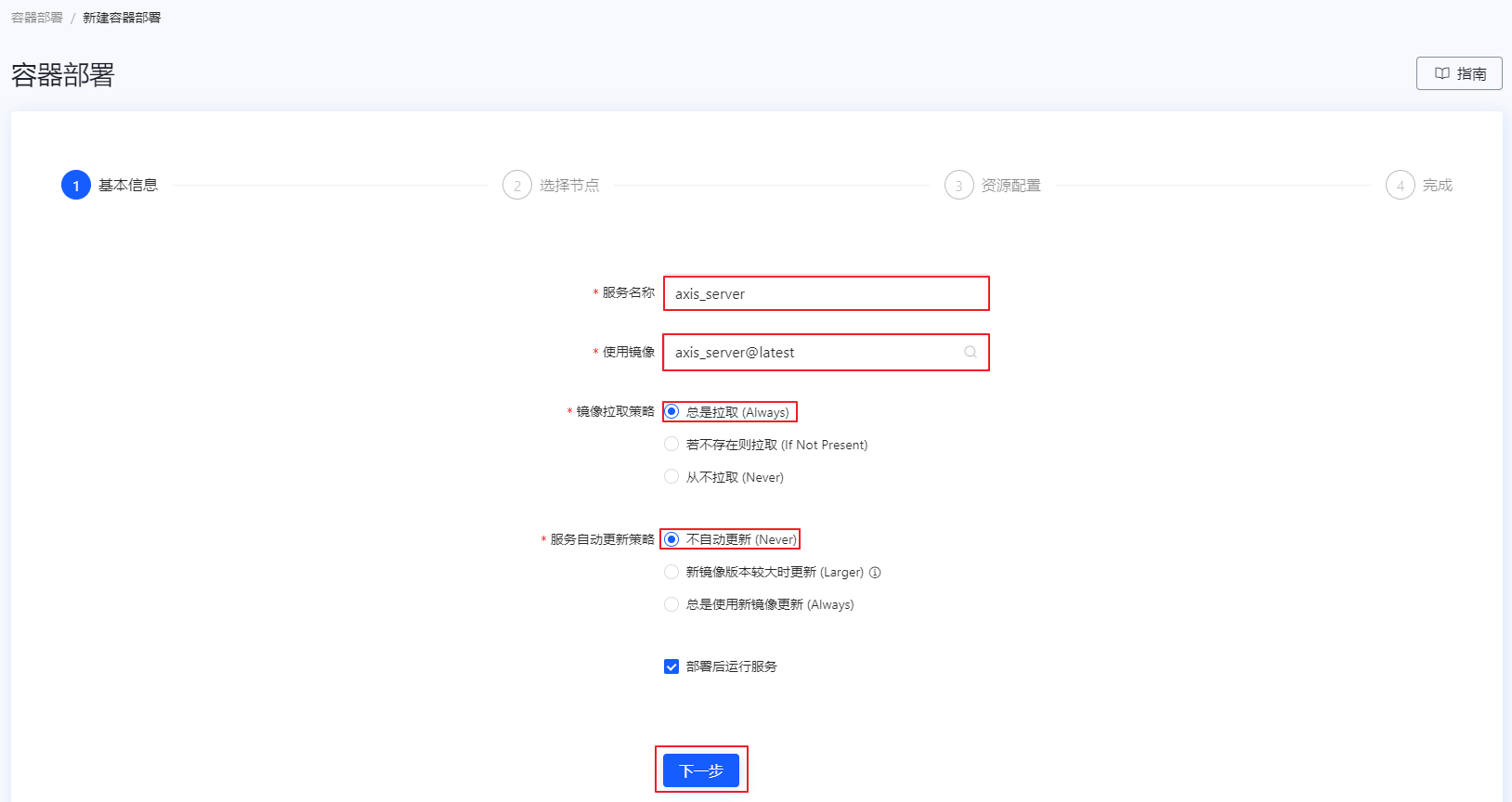
在选择节点界面,选择动态选择方式,节点数设置为 2,示例数设置为 1(1 个容器实例在 2 个节点上动态部署。
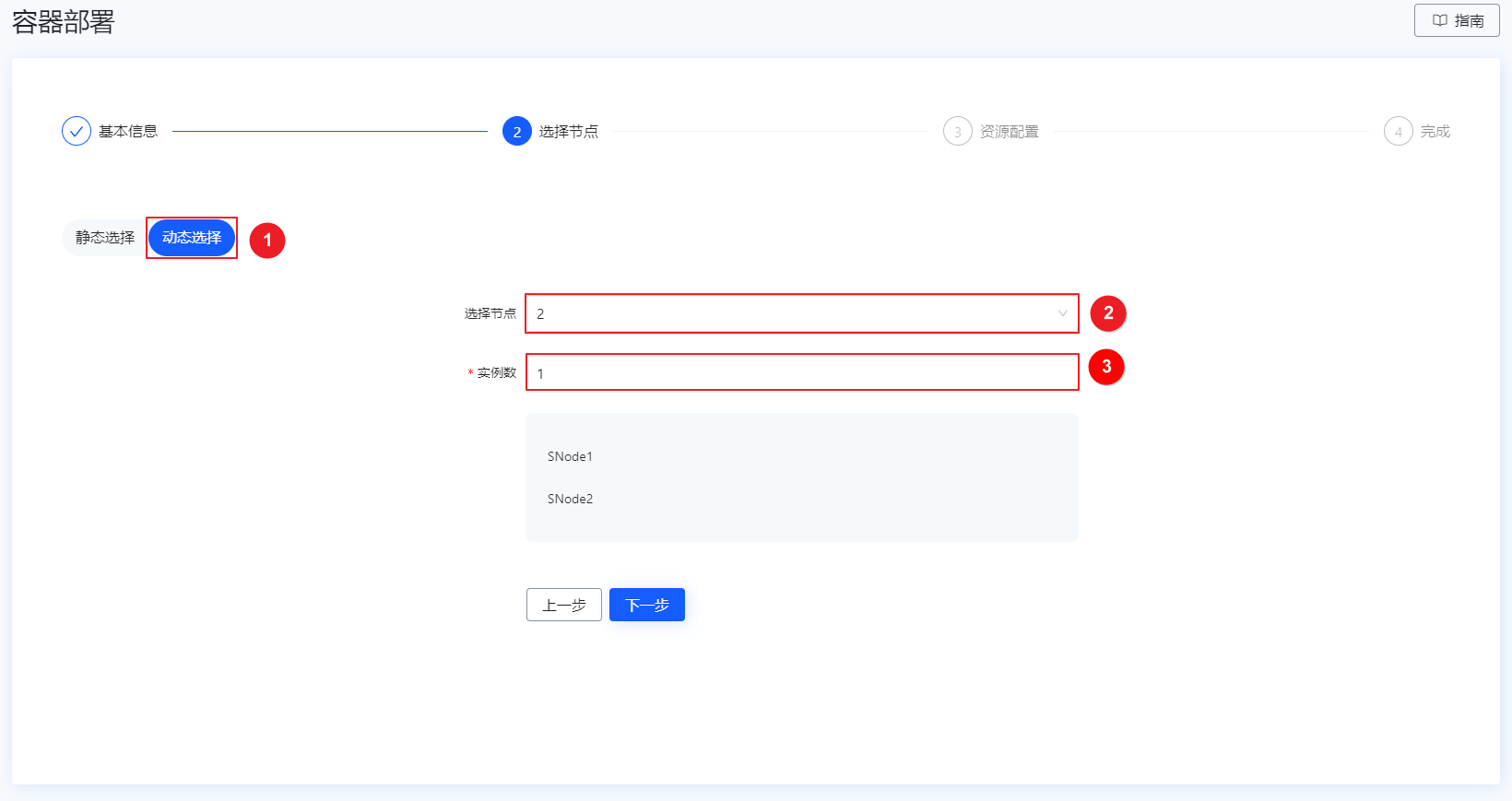
在资源配置界面,设置容器的资源配置参数,并单击部署,进入完成界面。
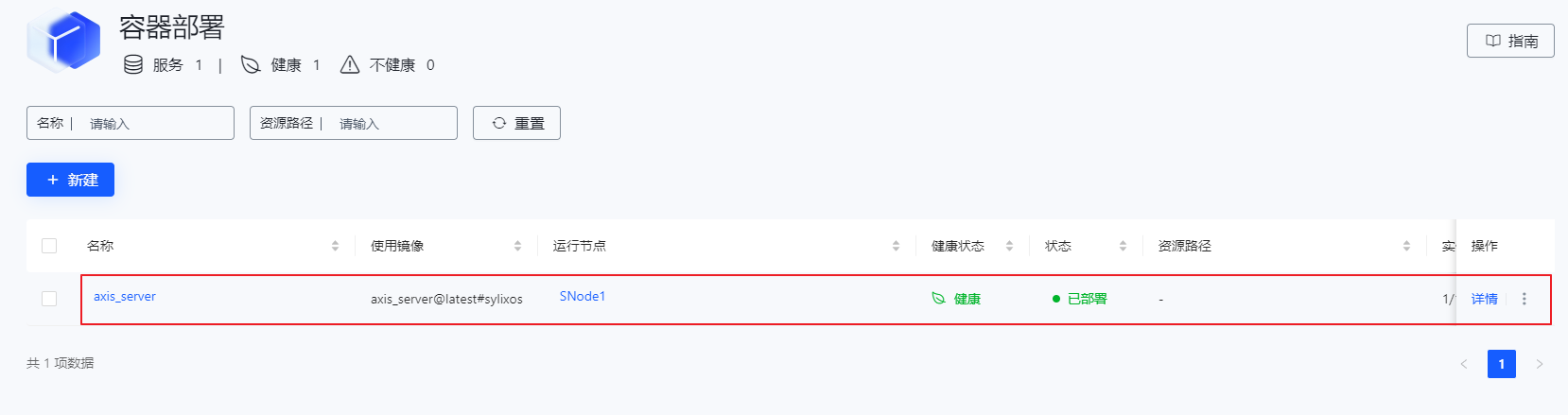
完成容器部署,新部署的容器会显示在容器部署页面的服务列表中。
触发动态迁移
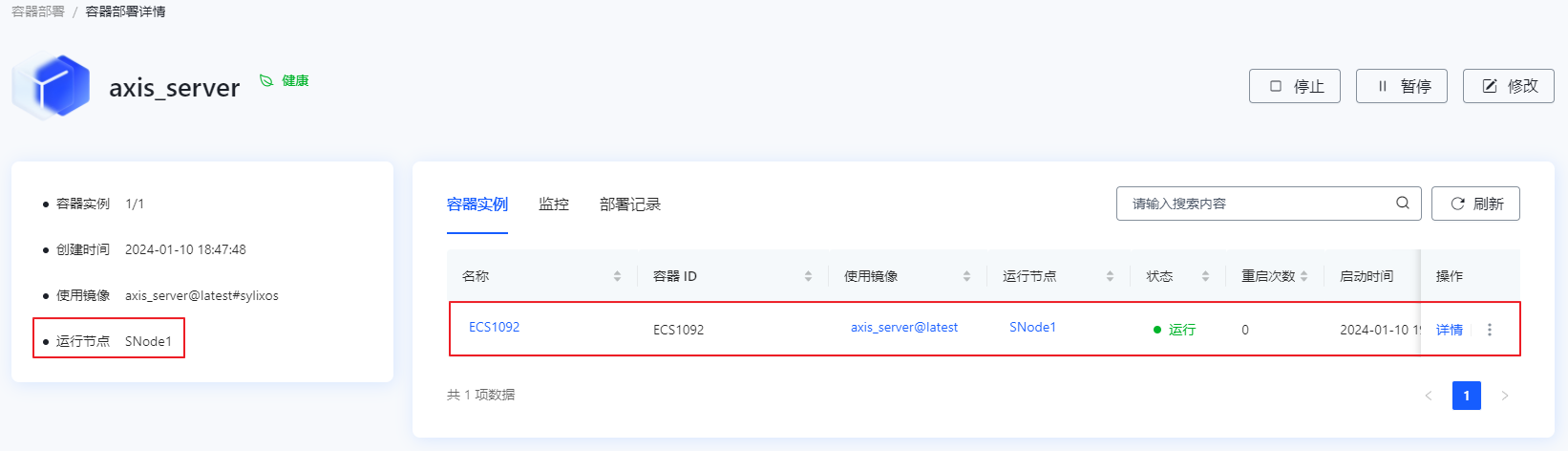
在 ECSM 平台查看 axis_server 服务动态选择节点运行容器实例情况,如下图所示,本次容器实例 ECSM 动态选择了 SNode1 首选运行节点(ECSM 动态选择策略是优先调度节点上运行容器实例少且剩余内存多的节点去处理作业任务)。
启动客户端 axis_client,客户端正常订阅和接收服务器端发布的陀螺仪数据。
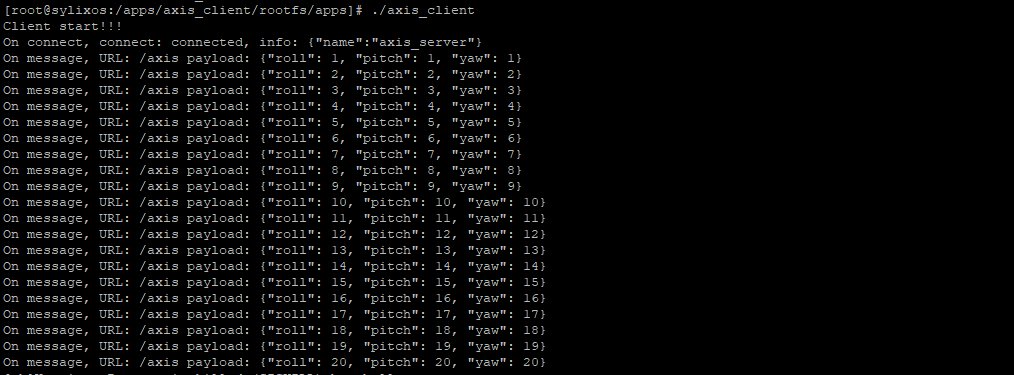
手动重启 SNode1 触发动态迁移功能。
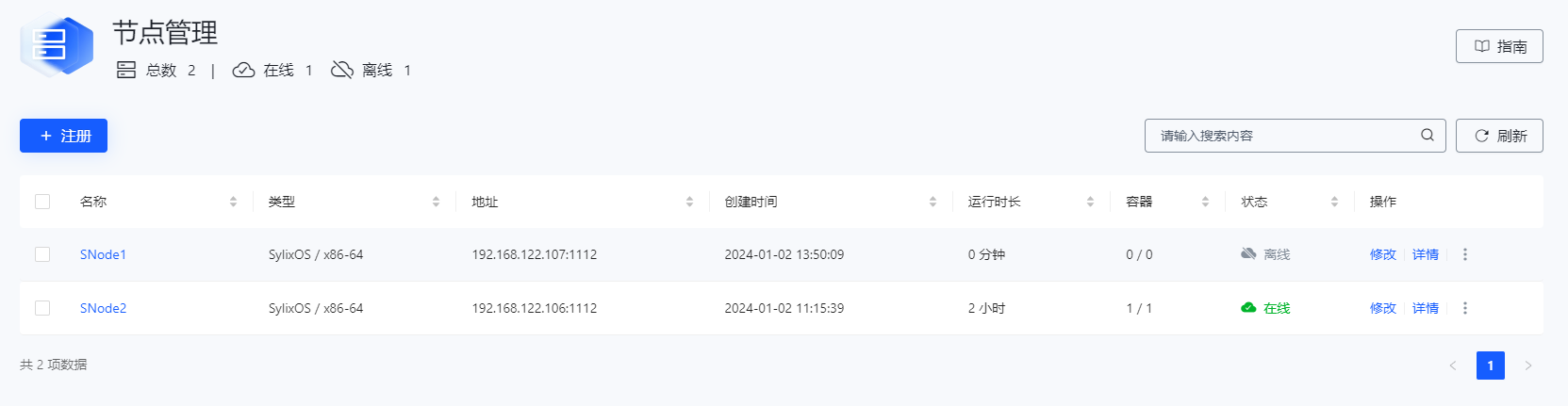
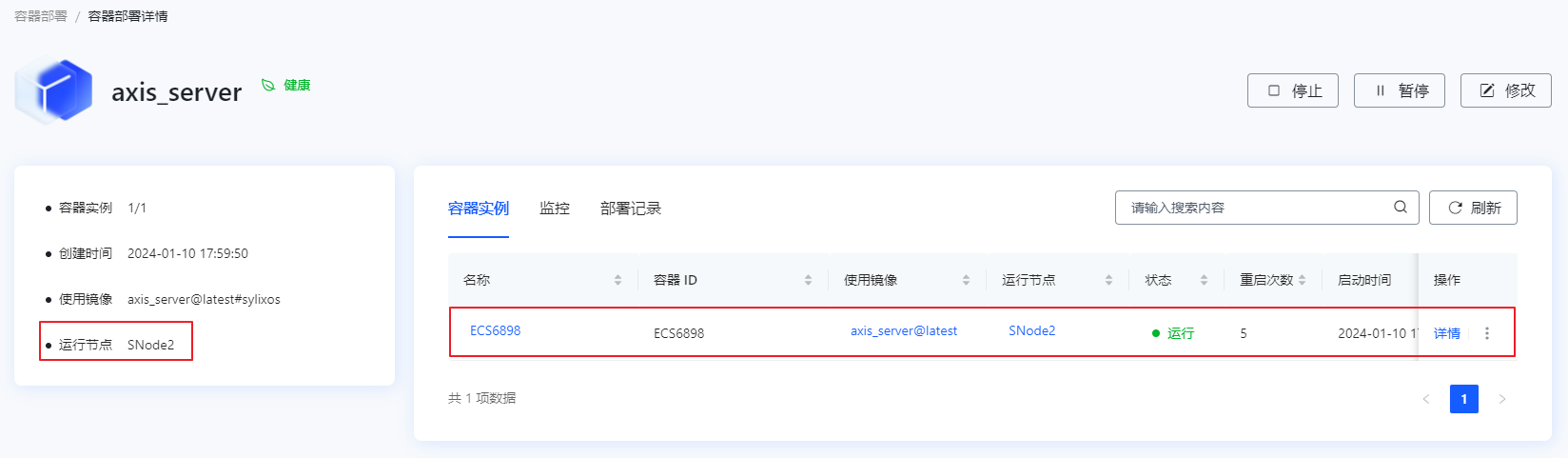
在容器部署界面查看 axis_server 迁移到 SNode2 节点上运行。
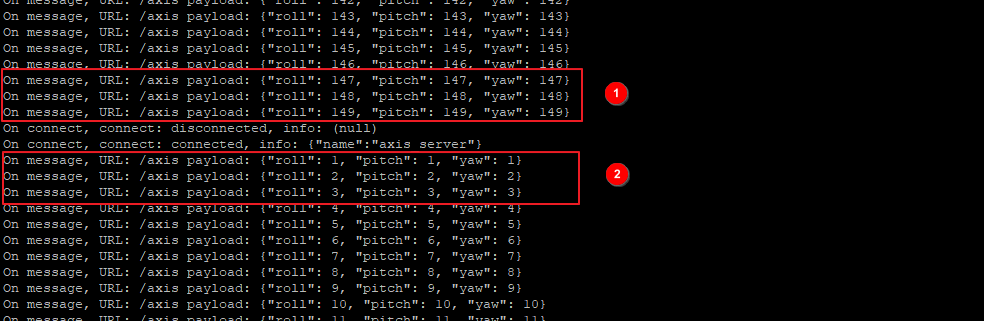
查看客户端 axis_client 回显页面,客户端已经订阅到 SNode2 节点上服务的数据。
 京公网安备11010802043204号
京公网安备11010802043204号