POSIX 条件变量
POSIX 条件变量的类型为 pthread_cond_t。使用时需要定义一个 pthread_cond_t 类型的变量,如:
pthread_cond_t cond;
POSIX 条件变量需要与 POSIX 互斥信号量结合使用,使用 POSIX 条件变量前,我们需要先创建一个用于共享资源锁用途的 POSIX 互斥信号量。
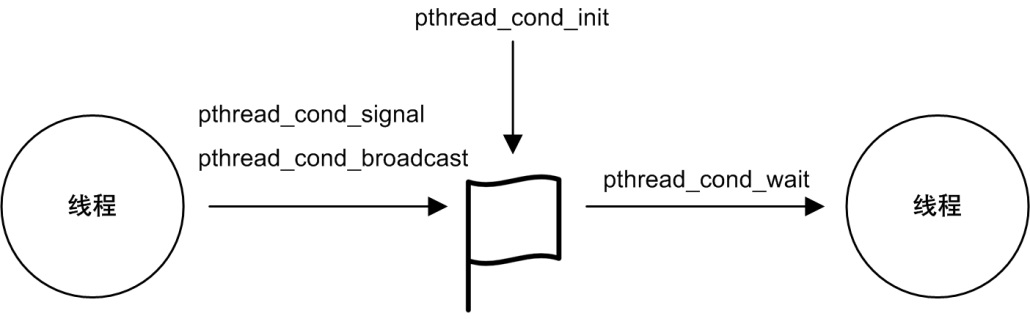
一个 POSIX 条件变量必须要调用 pthread_cond_init 函数初始化之后才能使用。
线程如果需要等待一个条件变量,可以调用 pthread_cond_wait 函数,中断服务程序不可以调用 pthread_cond_wait 函数等待一个条件变量,因为 pthread_cond_wait 函数会阻塞当前线程。
发送一个条件变量可以使用 pthread_cond_signal 或 pthread_cond_broadcast 函数,中断服务程序不可以发送一个 POSIX 条件变量。
当一个条件变量使用完毕后(并确保以后也不再使用),应该调用 pthread_cond_destroy 函数删除它,SylixOS 会回收该条件变量占用的内核资源。
创建一个 POSIX 条件变量需要使用 POSIX 条件变量属性块。POSIX 条件变量属性块的类型为 pthread_condattr_t。使用时需要定义一个 pthread_condattr_t 类型的变量,如:
pthread_condattr_t condattr;
条件变量属性块
条件变量属性块的初始化和删除
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_condattr_init(pthread_condattr_t *pcondattr);
函数 pthread_condattr_init 原型分析:
- 此函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcondattr 是 POSIX 条件变量属性块的指针。
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_condattr_destroy(pthread_condattr_t *pcondattr);
函数 pthread_condattr_destroy 原型分析:
- 此函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcondattr 是 POSIX 条件变量属性块的指针。
设置和获取条件变量属性块的进程共享属性
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_condattr_setpshared(pthread_condattr_t *pcondattr,
int ishare);
函数 pthread_condattr_setpshared 原型分析:
- 此函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcondattr 是 POSIX 条件变量属性块的指针。
- 参数 ishare 标识了 POSIX 条件变量属性块是否进程共享。
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_condattr_getpshared(const pthread_condattr_t *pcondattr,
int *pishare);
函数 pthread_condattr_getpshared 原型分析:
- 此函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcondattr 是 POSIX 条件变量属性块的指针。
- 输出参数 pishare 标识了 POSIX 条件变量属性块是否进程共享。
设置和获取条件变量属性块的时钟类型
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_condattr_setclock(pthread_condattr_t *pcondattr,
clockid_t clock_id);
函数 pthread_condattr_setclock 原型分析:
- 此函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcondattr 是 POSIX 条件变量属性块的指针。
- 参数 clock_id 是时钟类型。
注意:
当前参数 clock_id 只能用宏 CLOCK_REALTIME。
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_condattr_getclock(const pthread_condattr_t *pcondattr, clockid_t *pclock_id);
函数 pthread_condattr_getclock 原型分析:
- 此函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcondattr 是 POSIX 条件变量属性块的指针。
- 输出参数 clock_id 是时钟类型。
条件变量
条件变量的初始化和删除
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *pcond,
const pthread_condattr_t *pcondattr);
函数 pthread_cond_init 原型分析:
- 此函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcond 是 POSIX 条件变量的指针。
- 参数 pcondattr 是 POSIX 条件变量属性块的指针,可以为 NULL。
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *pcond);
函数 pthread_cond_destroy 原型分析:
- 此函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcond 是 POSIX 条件变量的指针。
条件变量的发送
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *pcond);
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *pcond);
以上两个函数原型分析:
- 函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcond 是 POSIX 条件变量的指针。
pthread_cond_broadcast 与 pthread_cond_signal 函数的区别在于,pthread_cond_broadcast 会以广播的方式唤醒阻塞在该条件变量的所有线程,而 pthread_cond_signal 只会唤醒一个线程。
条件变量的等待
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *pcond,
pthread_mutex_t *pmutex);
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *pcond,
pthread_mutex_t *pmutex,
const struct timespec *abs_timeout);
int pthread_cond_reltimedwait_np(pthread_cond_t *pcond,
pthread_mutex_t *pmutex,
const struct timespec *rel_timeout);
以上三个函数原型分析:
- 函数成功返回 0,失败返回错误号。
- 参数 pcond 是 POSIX 条件变量的指针。
- 参数 pmutex 是 POSIX 互斥信号量的指针。
- 参数 abs_timeout 是等待的绝对超时时间。
- 参数 rel_timeout 是等待的相对超时时间。
pthread_cond_timedwait 是 pthread_cond_wait 的带等待超时时间的版本,abs_timeout 为等待的绝对超时时间。
pthread_cond_reltimedwait_np 是 pthread_cond_timedwait 的非 POSIX 标准版本,参数 rel_timeout 为等待的相对超时时间。
下面程序展示了 POSIX 条件变量的使用,程序创建两个线程和一个 POSIX 互斥信号量及一个 POSIX 条件变量;线程 thread_a 对变量 count 打印,线程 thread_b 对变量 count 进行自增操作,使用 POSIX 互斥信号量作为访问变量 count 的互斥手段,使用 POSIX 条件变量作为变量 count 值改变的通知手段。
程序清单 POSIX条件变量的使用(POSIX_Conditional_Variable)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
static pthread_mutex_t lock;
static pthread_cond_t cond;
static int count = 0;
static void *thread_a (void *arg)
{
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &lock);
printf("thread_a(): count = %d\n", count);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
return (NULL);
}
static void *thread_b (void *arg)
{
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
count++;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
sleep(1);
}
return (NULL);
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t threada_tid;
pthread_t threadb_tid;
int ret;
ret = pthread_mutex_init(&lock, NULL);
if (ret != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "mutex create failed.\n");
return (-1);
}
ret = pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
if (ret != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "cond create failed.\n");
return (-1);
}
ret = pthread_create(&threada_tid, NULL, thread_a, NULL);
if (ret != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread create failed.\n");
return (-1);
}
ret = pthread_create(&threadb_tid, NULL, thread_b, NULL);
if (ret != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread create failed.\n");
return (-1);
}
pthread_join(threada_tid, NULL);
pthread_join(threadb_tid, NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
return (0);
}
在 SylixOS Shell 下运行程序:
# ./POSIX_Conditional_Variable
thread_a(): count = 1
thread_a(): count = 2
thread_a(): count = 3
thread_a(): count = 4
thread_a(): count = 5
thread_a(): count = 6
......
# ts
NAME TID PID PRI STAT LOCK SAFE DELAY PAGEFAILS FPU CPU
--------------------------- ------- ----- --- ---- ---- ---- ---------- --------- --- ---
POSIX_Conditional_Variable 401006c 34 200 JOIN 0 0 1 USE 0
pthread 401006d 34 200 SEM 0 0 0 0
pthread 401006e 34 200 SLP 0 212 0 0
 京公网安备11010802043204号
京公网安备11010802043204号