POSIX 自旋锁
自旋锁是为实现保护共享资源而提出一种轻量级的锁机制。其实,自旋锁与互斥锁比较类似,它们都是为了解决对共享资源的互斥访问。
无论是互斥锁,还是自旋锁,在任何时刻,最多只能有一个拥有者,也就说,在任何时刻最多只能有一个线程获得锁。但是两者在调度机制上有很大的不同。对于互斥锁,如果互斥锁已经被占有,申请者只能进入睡眠状态。但是自旋锁不会引起申请者睡眠,如果自旋锁已经被别的线程占有,申请者就一直在那里循环判断该自旋锁的拥有者是否已经释放该锁,“自旋”一词就是因此而得名。
由此我们可以看出,自旋锁是一种比较低级的保护数据结构或代码片段的原始方式,这种锁机制可能存在以下两个问题:
- 死锁:申请者试图递归地获得自旋锁必然会引发死锁。
- 消耗过多 CPU 资源 :如果申请不成功,申请者将一直循环判断,这无疑降低了 CPU 的使用率。
由此可见,自旋锁适用于锁使用者保持锁时间比较短的情况。信号量适用于保持锁时间较长的情况。
需要注意的是,被自旋锁保护的临界区代码执行时不能因为任何原因放弃 CPU,因此,在自旋锁保护的区域内不能调用任何可能引发系统任务调度的 API。
POSIX 自旋锁的类型为 pthread_spinlock_t。使用时定义一个 pthread_spinlock_t 类型的变量,如:
pthread_spinlock_t spin;
一个 POSIX 自旋锁必须要调用 pthread_spin_init 函数初始化之后才能使用。
线程如果需要等待一个自旋锁,可以调用 pthread_spin_lock 函数,中断服务程序不可以调用任何 POSIX 自旋锁 API。释放一个自旋锁可以调用 pthread_spin_unlock 函数。
当一个自旋锁使用完毕后(并确保以后也不再使用),应该调用 pthread_spin_destroy 函数将其删除,SylixOS 会回收该自旋锁占用的内核资源。
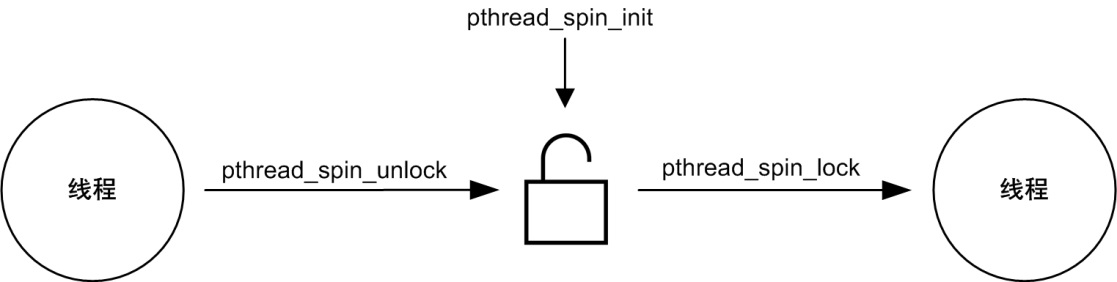
自旋锁
自旋锁的初始化和删除
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_spin_init(pthread_spinlock_t *pspinlock, int pshare);函数 pthread_spin_init 原型分析:
- 此函数成功时返回 0,失败时返回错误号。
- 参数 pspinlock 是 POSIX 自旋锁的指针。
- 参数 pshare 标识了 POSIX 自旋锁是否进程共享。
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_spin_destroy(pthread_spinlock_t *pspinlock);函数 pthread_spin_destroy 原型分析:
- 此函数成功时返回 0,失败时返回错误号。
- 参数 pspinlock 是 POSIX 自旋锁的指针。
自旋锁的加锁与解锁
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_spin_lock(pthread_spinlock_t *pspinlock); int pthread_spin_unlock(pthread_spinlock_t *pspinlock); int pthread_spin_trylock(pthread_spinlock_t *pspinlock);以上函数原型分析:
- 函数成功时返回 0,失败时返回错误号。
- 参数 pspinlock 是 POSIX 自旋锁的指针。
pthread_spin_trylock 是 pthread_spin_lock 的“尝试等待”版本,在 POSIX 自旋锁已经被占有时,pthread_spin_lock 将“自旋”,而 pthread_spin_trylock 将立即返回。
这时,POSIX 自旋锁的解锁操作只能调用 pthread_spin_unlock 函数。
如果中断服务程序也可能使用 POSIX 自旋锁保护的资源,应该使用带中断屏蔽版本的 POSIX 自旋锁 API,否则会发生死锁:
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_spin_lock_irq_np(pthread_spinlock_t *pspinlock, pthread_int_t *irqctx); int pthread_spin_unlock_irq_np(pthread_spinlock_t *pspinlock, pthread_int_t irqctx); int pthread_spin_trylock_irq_np(pthread_spinlock_t *pspinlock, pthread_int_t *irqctx);以上几个函数原型分析:
- 函数成功时返回 0,失败时返回错误号。
- 参数 pspinlock 是 POSIX 自旋锁的指针。
- 参数 irqctx 是 pthread_int_t 类型的指针,用于保存和恢复 CPU 的中断屏蔽寄存器。
pthread_spin_trylock_irq_np 是 pthread_spin_lock_irq_np 的“尝试等待”版本,在 POSIX 自旋锁已经被占有时,pthread_spin_lock_irq_np 将“自旋”,而 pthread_spin_trylock_irq_np 将立即返回。
这时,POSIX 自旋锁的解锁操作只能调用 pthread_spin_unlock_irq_np 函数。
下面程序展示了 POSIX 自旋锁的使用,程序创建两个线程和一个 POSIX 自旋锁,两个线程分别对变量 count 进行打印和自增操作,使用 POSIX 自旋锁作为访问变量 count 的互斥手段。
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> static pthread_spinlock_t lock; static int count = 0; static void *thread_a (void *arg) { int value; while (1) { pthread_spin_lock(&lock); value = count; pthread_spin_unlock(&lock); printf("thread_a(): count = %d\n", value); sleep(1); } return (NULL); } static void *thread_b (void *arg) { while (1) { pthread_spin_lock(&lock); count++; pthread_spin_unlock(&lock); sleep(1); } return (NULL); } int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { pthread_t threada_tid; pthread_t threadb_tid; int ret; ret = pthread_spin_init(&lock, FALSE); if (ret != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "mutex create failed.\n"); return (-1); } ret = pthread_create(&threada_tid, NULL, thread_a, NULL); if (ret != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "pthread create failed.\n"); return (-1); } ret = pthread_create(&threadb_tid, NULL, thread_b, NULL); if (ret != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "pthread create failed.\n"); return (-1); } pthread_join(threada_tid, NULL); pthread_join(threadb_tid, NULL); pthread_spin_destroy(&lock); return (0); }在 SylixOS Shell 下运行程序:
# ./POSIX_Spinlock thread_a(): count = 0 thread_a(): count = 1 thread_a(): count = 2 thread_a(): count = 3 thread_a(): count = 4 thread_a(): count = 5 thread_a(): count = 6 ...... # ts NAME TID PID PRI STAT LOCK SAFE DELAY PAGEFAILS FPU CPU ---------------- ------- ----- --- ---- ---- ---- ---------- --------- --- --- POSIX_Spinlock 401008f 44 200 JOIN 0 0 1 USE 0 pthread 4010090 44 200 SLP 0 626 0 0 pthread 4010091 44 200 SLP 0 626 0 0
 京公网安备11010802043204号
京公网安备11010802043204号